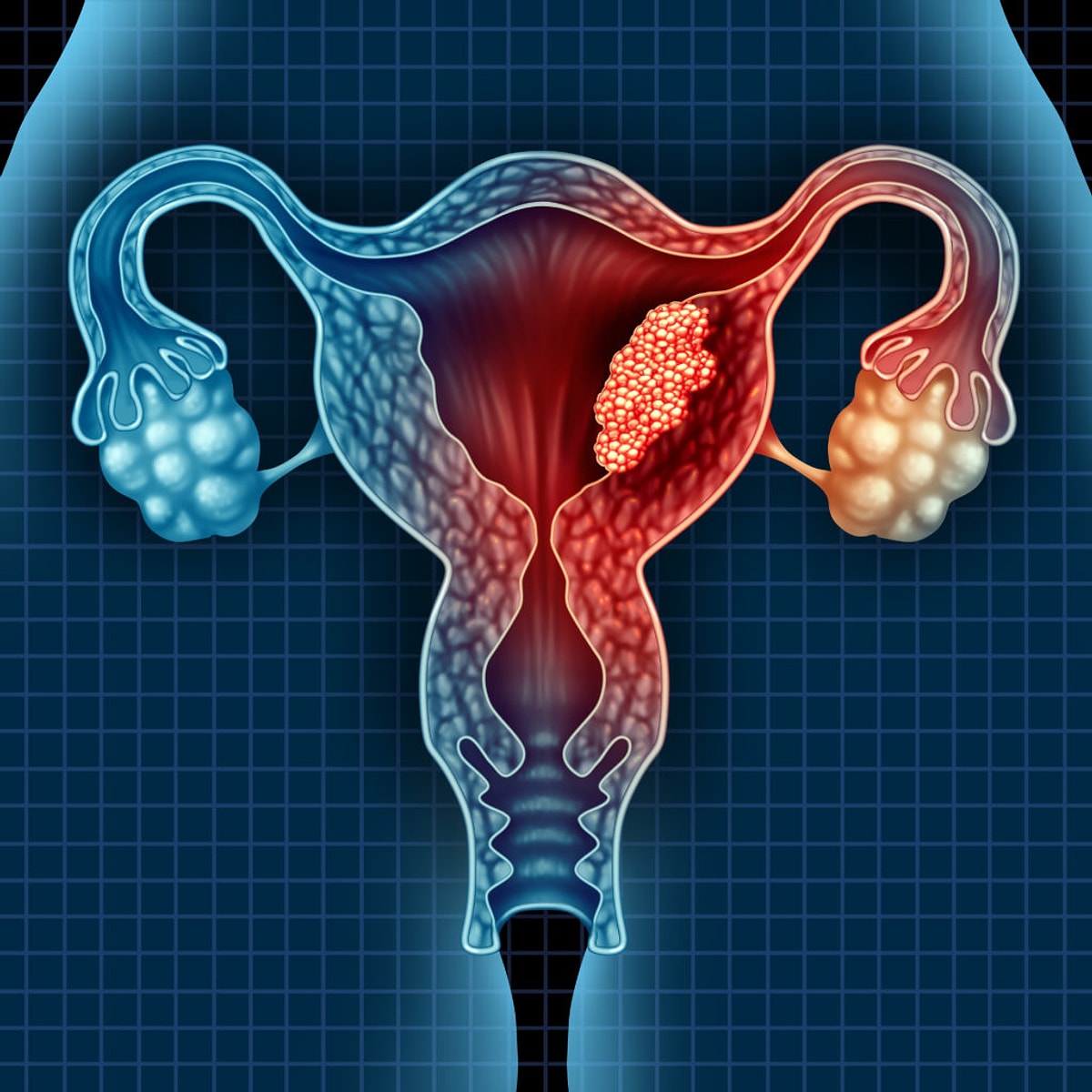
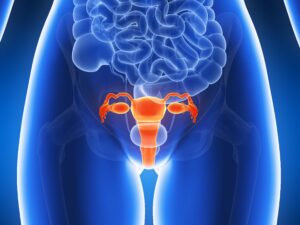
It is a disease caused by the uncontrolled growth of cells in the inner layer of the uterus. Uterine cancer, is usually seen in postmenopausal women. Abnormal vaginal bleeding is the most common symptom in the early stages. Although the exact cause is unknown, genetic predisposition is a risk factor. Treatment methods include surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Early diagnosis increases the success of treatment. It is important to consult a doctor.
What are the symptoms of uterine cancer?
It may indicate abnormal, foul-smelling or bloody vaginal discharge. Symptoms such as burning during urination, frequent urination, and irregular bowel movements are observed. General symptoms such as unexplained weight loss and constant fatigue are signs of a serious health problem. If these symptoms are present, an appointment should be made with a gynecologist in postmenopausal women. A definitive diagnosis can be made with diagnostic methods such as transvaginal ultrasound and biopsy. Uterine cancer Early diagnosis is critical to the success of treatment.
What Causes Uterine Cancer?
The hormones estrogen and progesterone play an important role in uterine health. An imbalance between these hormones can cause the uterine wall to thicken excessively. This can increase the risk. Especially in the postmenopausal period, high estrogen levels are a risk factor. Excess weight causes estrogen levels in the body to increase. Fat tissue increases estrogen production uterine cancer may increase the risk of developing. Polycystic ovary syndrome can cause hormonal imbalances. In the long term, it can increase the risk.
Women who have irregular menstrual periods have also been observed to have an increased risk. People with a family history of ovarian cancer are at higher risk due to genetic predisposition. Birth control pills contain progesterone, which can reduce the risk. Women who do not use these pills may experience an increased risk. Early menstruation and late menopause cause the uterus to be exposed to the estrogen hormone for a longer period of time. This can increase the risk. Diabetes can affect hormone balances, which can increase the risk.
People with diabetes are at higher risk. Tamoxifen, a drug used to treat breast cancer, may slightly increase the risk. However, the benefits of this drug generally outweigh the risks. Radiation therapy to the pelvic area causes cellular damage to the uterine tissue. Uterine cancer triggers its development. Having one or more of the risk factors does not necessarily mean that this disease will develop. However, being aware of these risk factors and having doctor check-ups are very important for early diagnosis.
How Is Uterine Cancer Treated?
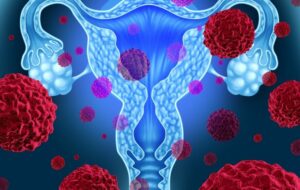
Treatment is usually planned according to the stage of the disease and the patient's condition. Sometimes it can also be treated with hormone therapy. Hormone suppression therapy can be applied to types of cancer that are sensitive to hormone receptors. Biological treatment methods focus on certain genetic characteristics of the cancer. It can provide targeted treatment. The treatment process is planned with a multidisciplinary approach. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the stage of the cancer, its type, the patient's age and general health status. Uterine cancer Early diagnosis increases the chance of success in treatment. Therefore, regular check-ups and screenings are important.